This blog has moved to a new website
Nutrition, Health & Wellness
Home > Coping with Pregnancy-related pelvic girdle pain
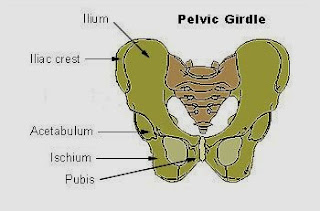
The pelvic girdle is the largest part of our skeleton containing the pubic symphysis, and two sacroiliac joints. A net work of ligaments join these three joints giving them strength. We have to note that pregnancy-related low-back pain, sciatica, visceral or vascular origin syndromes are distinct entities which needs to be excluded before the diagnosis of PPGP is made. European guidelines recommended MRI scan for the differential diagnosis of PPGP in all stages.
Signs and symptoms during pregnancy
PPGP is associated with dull, stabbing, shooting or burning pain in pelvic girdle area during pregnancy. It may be spread over the general area of the girdle. It may also be localized either posteriorly close to the sacroiliac joints (hips and buttocks) or anteriorly to the symphysis pubis area (groin). Some of the symptoms are:- Inflammation of the joints in the pelvic girdle.
- Tenderness in the pubic bone area.
- Difficulty in standing on one leg.
- Difficulty in lifting leg.
- Difficulty keeping legs or knees apart.
- Stooping backward when standing.
- Difficulty in twisting, bending or squatting.
- Pain may radiate to the legs.
- Alteration of gait patterns.
- Clicking sound or sensation from the pelvic girdle during movement.
Pelvic girdle pain in pregnancy - possible causes
The exact causes leading to the development of this syndrome are unclear. Etiological implications may be multifactorial conditions during pregnancy like hormonal changes, bio-mechanical factors, trauma, metabolic changes and genetic factors. The release of pregnancy hormones, structural and postural changes in pregnancy, gait changes, weight of the growing baby and changes in the center of gravity can all add to the development of PPGP. Having PPGP in a previous pregnancy predisposes the person to have pelvic girdle pain in subsequent pregnancy.Any change during pregnancy in the activity of the muscles in pelvic girdle, hips (hip abductor and hip extensor), lower back, abdomen, ankle (ankle plantar flexor) and pelvic floor can cause this condition. Remodeling of soft tissues, cartilage and ligaments over time or due to pregnancy by bio-mechanical and hormonal factors can also contribute to development of this discomfort.
Treatment for pregnancy related pelvic girdle pain
Many treatment options like exercises, exercises in water, physiotherapy, chiropractic manipulations, medication, educational interventions, acupuncture, use of mobility aids, and intensive multidisciplinary bio-psycho-social rehabilitation treatment are available. For very severe debilitating cases during pregnancy surgical treatment (fusion surgery) is considered. The available treatment options during pregnancy are limited by the presence and the potential hazards to the fetus.Coping with pelvic girdle pain in pregnancy
Self care and management can to a great extend contribute in the alleviation of the distressing condition.- Take care to have sufficient rest.
- Avoid lying on your back.
- Lie on your side with a pillow between your knees to keep hip joints aligned.
- Avoid sitting slumped.
- Be active within the pain limits.
- Avoid strenuous activities.
- Avoid weight bearing activities.
- Avoid climbing stairs.
- Wear flat shoes.
- Avoid twisting, bending or squatting.
- Take small steps while walking.
- Avoid any action or movement with knees apart.
- As far as possible Keep the knees together.
- Avoid stressing the joints.
- For getting into bed, sit on the edge keeping the knees close together and lie down on your side by simultaneously lifting your feet.
- Do the reverse of it when getting out of bed.
- While shifting position in the bed keep the knees together.
- Avoid moving your knees apart.
- Avoid standing on one leg.
- Avoid carrying a baby on one hip during pregnancy.
- Consider wearing hip support.
With the increase in clinical awareness of pregnancy related hip girdle pain syndrome and multidisciplinary medical approach there are significant improvements in the treatment and management of this multifactorial syndrome.
References:
1. Wu W, Meyer O, Uegaki K et al. 2004. Pregnancy-related pelvic girdle pain, 1: terminology, clinical presentation and prevalence. Eur Spine Journal Epub 13: 575-589
2. Vleeming A, Vries HJD, Mens JMA et al. 2002. Possible role of the long dorsal sacroiliac ligament in women with peripartum pelvic pain. Acta Obstetrica Gynecologica Scandinavica 81: 430-436
3. Nikolaos K Kanakaris, Craig S Roberts and Peter V Giannoudis. Pregnancy-related pelvic girdle pain: an update BMC Med. 2011; 9: 15. Published online 2011 February 15.
Interesting topics on fitness tips:
Severe hypothyroidism.
Chronic sinusitis treatments.
Health benefits of cloves.
Back pain from backpacks.
Celery Nutrients.
Barley grass juice.
Aspirin for cancer prevention.
MRI benefits.
Yo-yo effect.
Causes of frequent headaches.
Severe hypothyroidism.
Chronic sinusitis treatments.
Health benefits of cloves.
Back pain from backpacks.
Celery Nutrients.
Barley grass juice.
Aspirin for cancer prevention.
MRI benefits.
Yo-yo effect.
Causes of frequent headaches.
License: Public domain.
Current topic on health tips:
Coping with pelvic girdle pain during pregnancy.